Put Options
What is a Put Option?
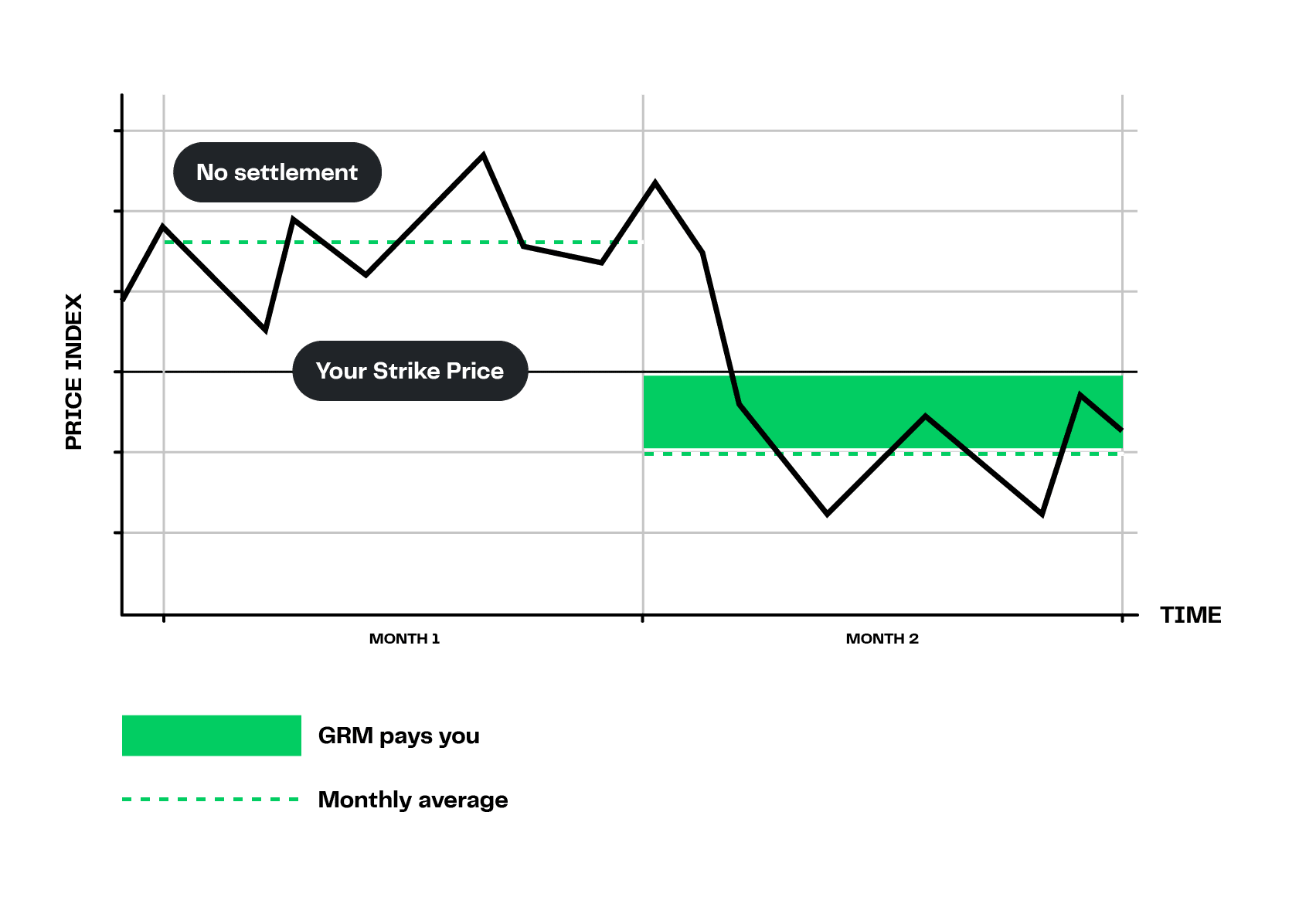
Put options serve as a financial safeguard in energy markets, allowing businesses to protect themselves against falling prices. When a company purchases a put option, it gains the right to sell a specific amount of energy (such as oil, natural gas, or electricity) at a set price, known as the strike price, before a certain date.
This tool is particularly valuable for energy producers, such as oil companies or utilities, whose revenues can be severely impacted by sudden drops in energy prices. By using put options, these businesses can effectively set a floor on their selling price, ensuring more predictable income.
For example, a trader might purchase put options to hedge against potential declines in commodity prices. If the price falls below the strike price, the trader can exercise the option to sell at the higher, predetermined rate. If prices remain high, the trader allows the option to expire, having only incurred the initial premium cost.
Does your company need energy hedging?
Here are 4 reasons you do!
- Protect from unexpected changes
- Budget & contract security
- Focus on your core business
- Shine in front of stakeholders
Put Options vs. Call Options
- Put Options: These give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) within a specified period. Put Options are typically used to hedge against or speculate on a decrease in the asset’s price.
- Call Options: In contrast, Call Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy an asset at a predetermined price within a specified period. They are generally used to hedge against or speculate on an increase in the asset’s price.
The strategic use of Put Options can protect against downside risks, while Call Options can protect against upside risks, offering a balanced approach to managing energy price volatility.
Stay Ahead of the Curve with
GRM Market Insights
In the fast-paced world of energy trading, knowledge is power!
Our Market Insights give you the edge with analysis and expert forecasts.
Practical applications: Hedging in energy markets
Hedging with Put Options is a common practice among companies involved in the production, distribution, and intensive use of energy commodities. These companies face substantial risks from price fluctuations, and Put Options provide a mechanism to manage these risks effectively.
- Producers: For example, an Energy Supply company might use Put Options to ensure a minimum selling price for its asset. In the event of a price drop due to geopolitical instability or other factors, the company can exercise the Put Options and sell its asset at the more favourable strike price, thereby avoiding significant financial losses.
- Consumers: On the other hand, energy consumers such as airlines or shipping companies might leverage Put Options to cap fuel costs. Since fuel expenses represent a large portion of their operational costs, securing a maximum price for fuel can protect against unexpected surges in oil prices, providing more predictable budgeting and financial planning.
The role of market analysis
Effective utilization of Put Options in energy markets necessitates thorough market analysis. Energy consumers and traders must grasp not only the factors influencing commodity prices but also how these factors interact with global economic conditions.
Key areas of focus include:
- Supply-demand balance: Analyzing current and projected energy production levels against consumption trends is essential for anticipating potential price declines, which can inform Put Option strategies.
- Geopolitical factors: Political instability in energy-producing regions can significantly affect prices. Monitoring international relations and policy changes is crucial for making informed decisions regarding Put Options.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in energy efficiency, storage, and alternative energy sources can impact the demand for traditional energy commodities, influencing their pricing and the utility of Put Options.
- Seasonal patterns: Many energy commodities display cyclical price behavior. Understanding these patterns is vital for effectively timing Put Option purchases.
- Regulatory environment: Changes in environmental regulations, emissions standards, or energy policies can dramatically alter energy consumption patterns and prices, affecting the effectiveness of Put Options.
- Economic indicators: Broader economic trends, such as GDP growth rates or industrial production indices, can offer insights into future energy demand and potential price declines.
By conducting comprehensive market analysis, energy consumers can better determine when to purchase Put Options, at what strike prices, and for which expiration dates. This analysis aids in developing more effective hedging strategies and can potentially lower the overall cost of managing energy price risks.







